Anisotropic Conductive Adhesive Bonding
Revolutionizes microelectronics with high-performance bonding solutions designed for the evolving demands of modern technologies.
What are Anisotropic Conductive Adhesives (ACAs)?
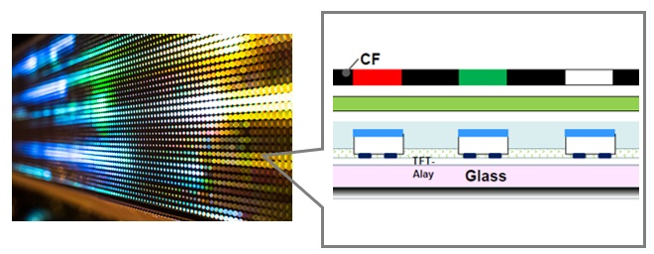
Structure of Anisotropic Conductive Film (ACF)
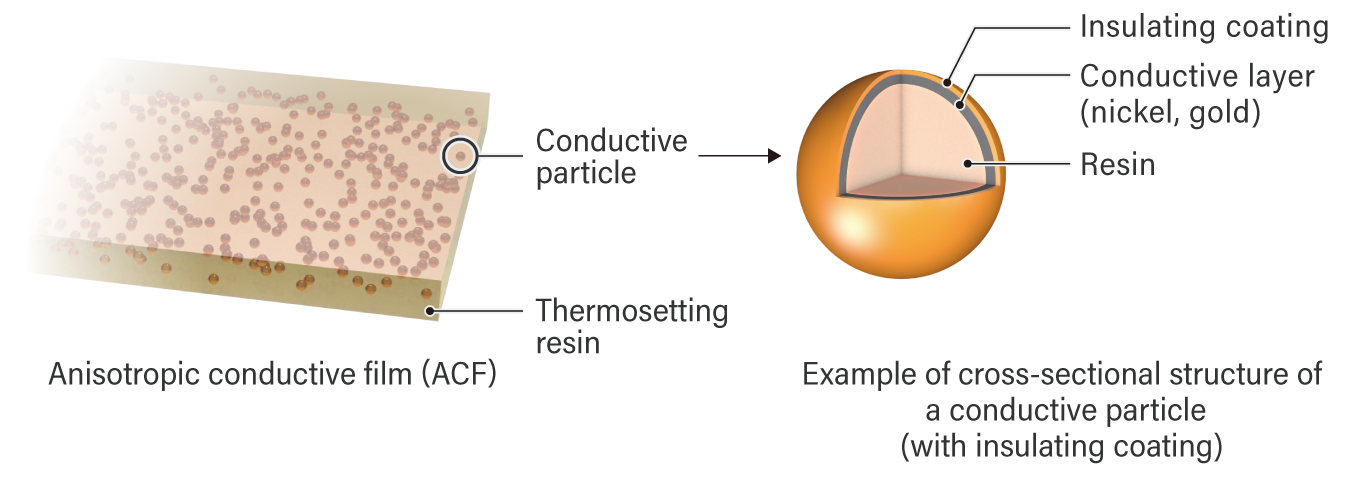
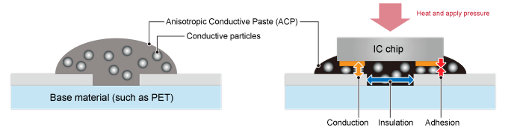
How ACF's bond, conduct and insulate
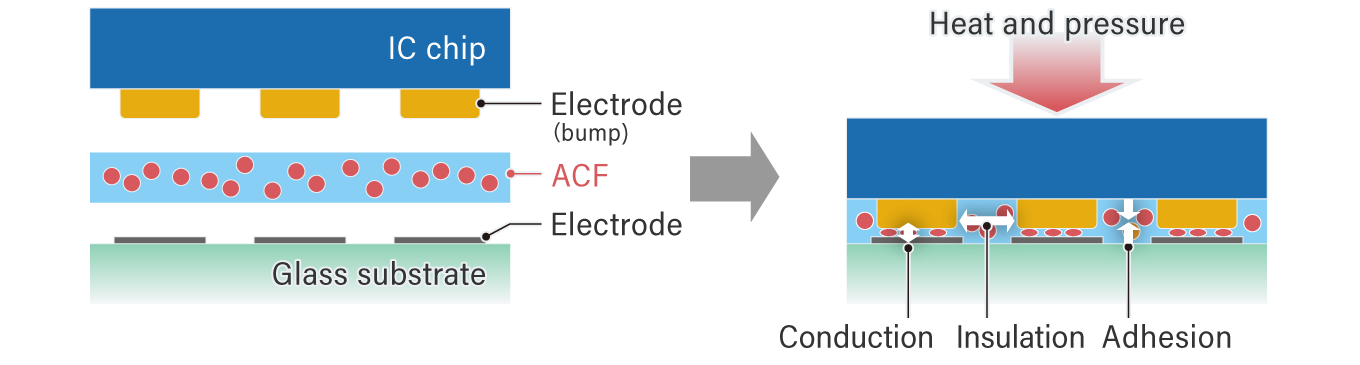
(Source: Dexerials Tech Times)
Anisotropic Conductive Adhesives (ACAs) offer several advantages in electronic packaging and display applications. Here are some key benefits:
Fine-Pitch Connectivity
Supports ultra-fine-pitch connections, making it ideal for compact and high-density circuits in modern electronics.
Low-Temperature Processing
Unlike soldering, ACAs cure at lower temperatures, reducing thermal stress on sensitive components like OLED displays and flexible circuits.
Lead-Free & Environmentally Friendly
ACAs are a RoHS-compliant alternative to traditional solder, eliminating lead and reducing environmental impact.
Reliable Electrical and Mechanical Bonding
Provides both strong adhesion and electrical conductivity, ensuring durable and stable connections.
They come in either a film (ACF) or paste form (ACP):
Anisotropic Conductive Adhesives (ACAs) are widely used in electronics and display technologies due to their ability to create precise electrical connections. Here are some key use cases:
Reliable Electrical and Mechanical Bonding
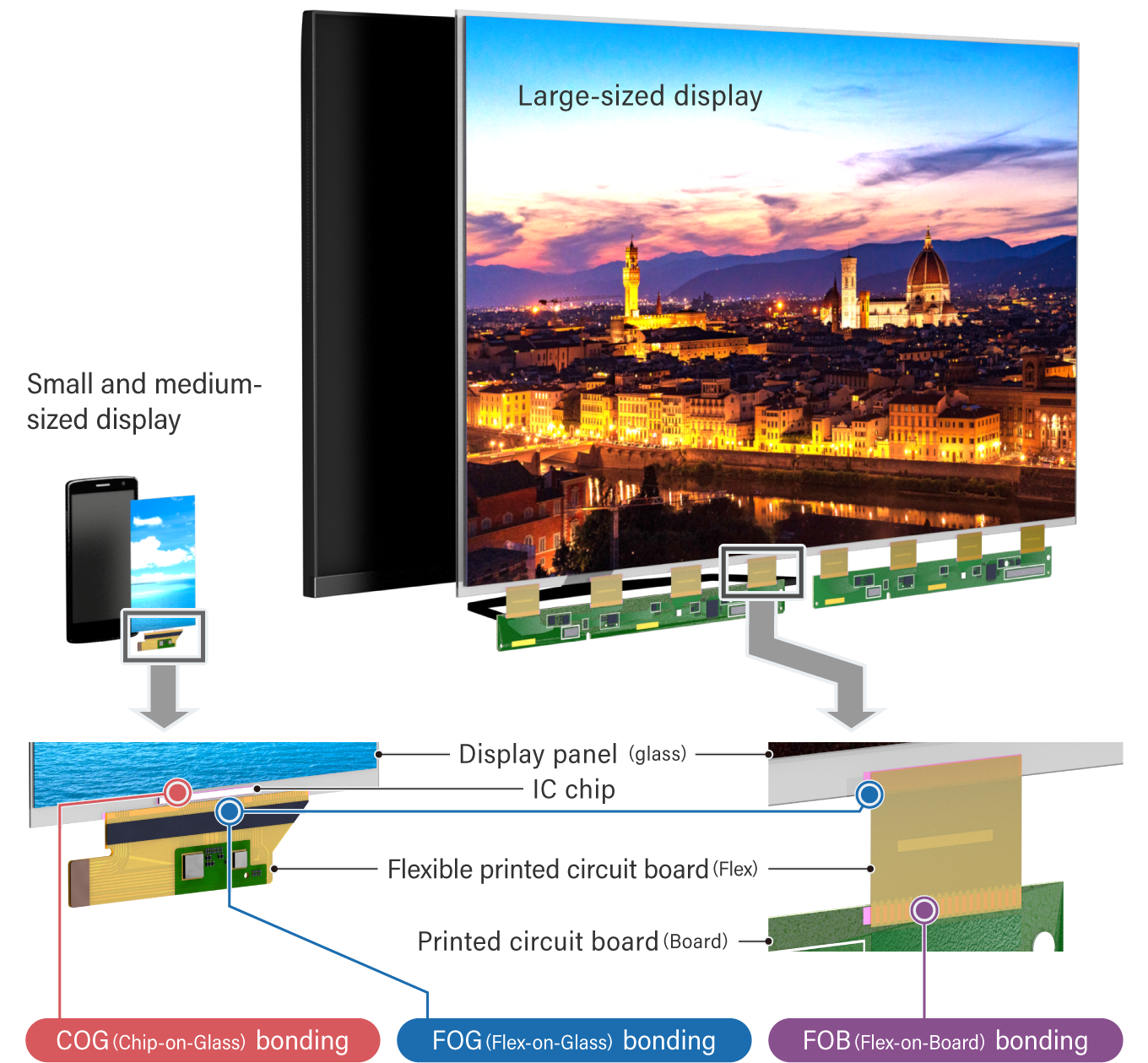
COG (Chip-on-Glass): Attaches ICs directly onto glass substrates in LCD and OLED displays
FOG (Flex-on-Glass): Connects flexible circuits to glass substrates, commonly used in touchscreens and automotive displays
FOB (Flex-on-Board): Bonds flexible circuits to rigid PCBs in display modules.
Anisotropic Conductive Film (ACF) use cases COG Bonding, FOG Bonding and FOB Bonding
(Source: Dexerials Tech Times)
Semiconductor Packaging
Flexible and Wearable Electronics
Enables connections in flexible circuits used in smartwatches, fitness trackers, and medical sensors.
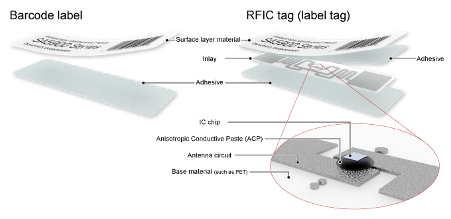
Smart Cards & RFID
Used in contactless payment cards, NFC tags, and RFID chips, ensuring reliable, ultra-thin electrical connections.
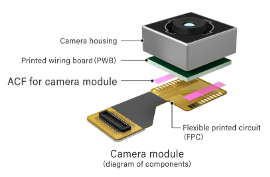
Camera Modules & Image Sensors
Bonds ICs in CCD (charge-coupled devices) and CMOS sensors (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductors) for smartphone and security cameras.
(Source: Dexerials Tech Times)
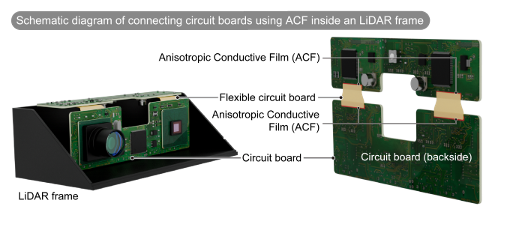
Automotive Electronics
Connects components in Head-Up-Displays (HUDs), Infotainment Systems and Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS).
(Source: Dexerials Tech Times)
LED & Micro-LED Assembly
Facilitates precise electrical interconnects in mini-LED and micro-LED display manufacturing.
(Source: Resonac)
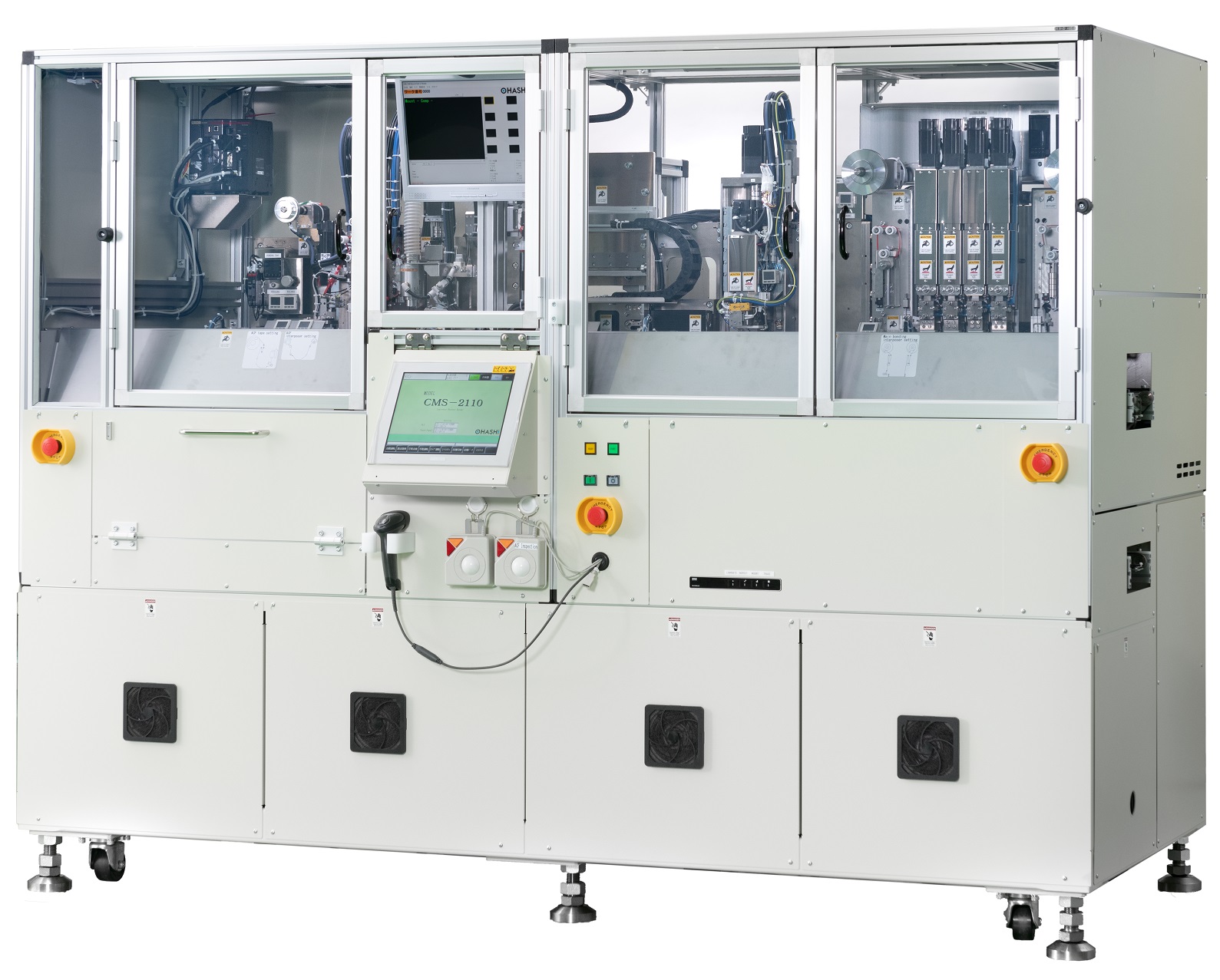
We offer proposals for in desktop, semi-automatic and fully-automatic equipment configurations for all kinds of ACAs Bonding applications.
Would like to learn more?
E-mail us: ieu@ito-group.com